Dielectrics-12
These are the insulators which when subjected to an external electric field, undergo polarization.
Dielectrics-12-Types of Dielectrics
As per the concepts of atomic models presented by various scholars at different times, the negative charge in the form of an electron cloud is distributed around the nucleus, having an equal positive charge due to the protons. These two types of charge distribution may be symmetric or asymmetric in nature. As such in an atom or molecule of a dielectric, the center of gravity of the positive and negative charges may or may not coincide. Therefore, the atoms or molecules of the dielectrics are termed non-polar or polar in Dielectrics-12
Dielectrics-12-Polar Dielectrics
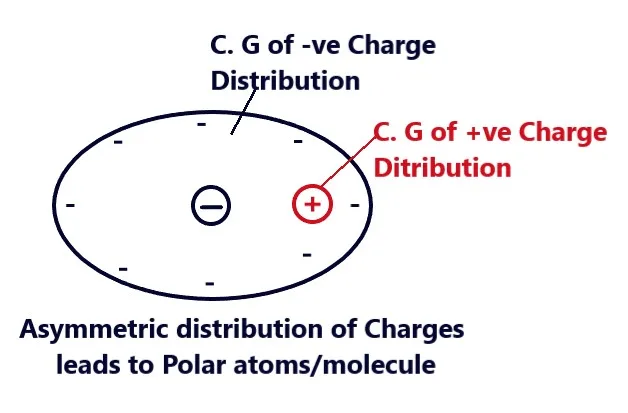
A Dielectric in the atoms or molecules of which the center of gravity of positive and negative charges do not coincide is called the polar dielectric. Therefore, in the atoms and molecules of a polar dielectric, the positive and negative charges possess an asymmetric charge distribution about their centers. Due to finite separation between the positive and negative charges, such atoms or molecules possess a finite electric dipole movement, the molecules such as NS3HCL, and H2O. CO2 etc. is an example of a polar molecule in Dielectrics-12
The water molecule has a permanent dipole moment of the order of 6. Cross 10 raise to the power minus 80 centimeters. In fact, molecules have normally an asymmetric distribution of charge. For example. In an ionic molecule, the electrons are transferred from one atom to some other atom in the molecule. The resulting molecule is therefore made of positive and negative ions in different locations and must possess an electric dipole moment.
Dielectrics-12-Non-Polar Dielectrics
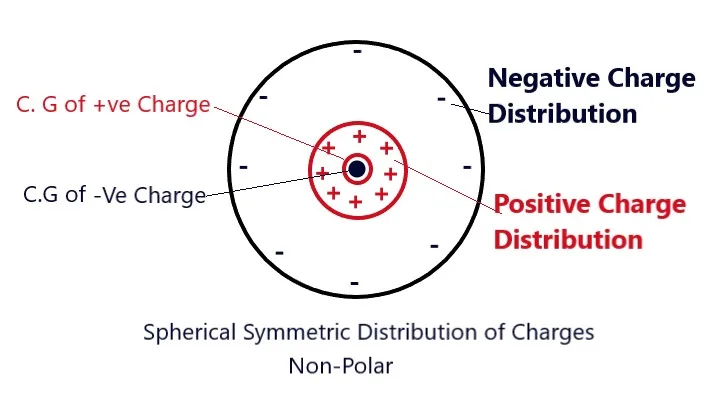
A dielectric in the atoms or molecules of which the center of gravity of positive and negative charges coincide is called a non-polar dielectric. Thus, in atoms or molecules of non-polar dielectrics, these positive and negative charges have a symmetrical charge distribution about their centers due to zero separation between the positive and negative charges. The electric dipole moment of such atoms or molecules is zero.
Dielectrics-12-Polarization of non-polar dielectric atoms
When a non-polar atom is subjected to an electric field, the positive nucleus gets pulled along the direction of the electric field, while electrons get pulled in the opposite direction. Due to this, restoring force is set up so as to bring the electron cloud back to its original state with respect to the nucleus.
The stretching of the atom continues till the restoring force becomes just equal and opposite to the force exerted by the applied electric fields on the charge. The stretching of dielectric atoms due to the displacement of the charges in the atoms under the action of the applied electric field is called polarization. As a result of the stretching of the atom, the center of gravity of the positive nucleus does not coincide with that of negative electrons. Due to this, the atom acquires a dipole moment.
Dielectrics-12-Polarization of Dielectric Slab
Consider a parallel plate capacitor connected to a steady source of emf (battery) that is allowed to be charged so that an electric field of strength E0 is set up between the plates of the capacitor enclosing the air

Suppose that a dielectric slab of non-polar atoms is introduced between the two plates of the capacitor. As soon as the dielectric slab is introduced, each molecule of the dielectric gets polarized. Therefore, the center of gravity of positive charge distribution within the nucleus and negative charges distribution due to the extranuclear electrons getting displaced from each other. On the left face of the dielectric slab, a net negative charge -qi, and on its right face, a positive charge +qi appears.
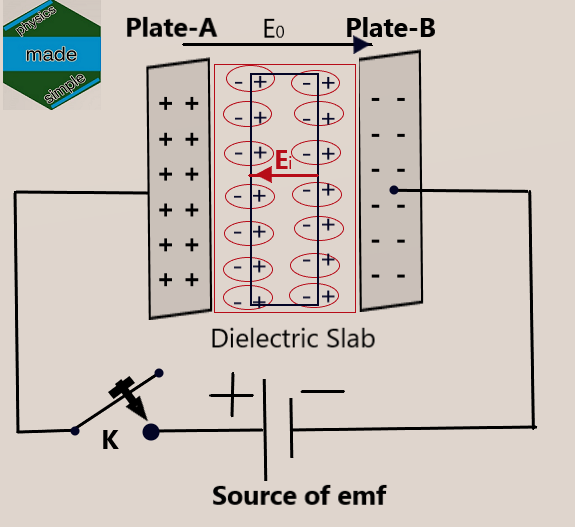
There is no net charge in the interior of the dielectric slab marked by the boundary marked in red color. The charges. -qi and +qi on the two faces of the dielectric slab is called induced charges. The induced charges set up an electric field Ep, is inside the dielectric. It is called an electric field due to polarization. The direction of the electric field due to polarization is from positive to negative induced charges developed on the two faces of the dielectric slab. Therefore, along a direction, opposite to the direction of the applied electric field, E 0. Therefore, the resulted in the electric field at. Electric is given by.
E = E0 – Ep – – – – 02
It can be concluded that the strength of the electric field between the two plates gets reduced on placing a dielectric slab and so E is called as reduced value of the electric field.
Dielectrics-12-Dielectric Constant
The Dielectric Constant of a dielectric medium is defined as the ratio of the strength of the applied electric field to the strength of the reduced value of the electric field on placing the dielectric medium between the plates of the capacitor. It is also known as relative permittivity or specific inductive capacity and is denoted by K. Therefore, a dielectric constant of a dielectric medium is given by the equation.
K = E0 /E – – – – -03
Since (E0 / E) > 1 Thus, the dielectric constant K is always greater than one (unity)
Dielectrics-12-Polarization density
Polarization density (P) is defined as the electric dipole moment induced in a dielectric slab per unit of its volume when placed inside the electric field. It is represented as,
P = N p – – -04
Where, P, N, and p are called polarization density, no. of atoms per unit volume, and induced dipole moment respectively. Let A be the area of each plate of the capacitor and d is the distance between the plates so that the volume of the dielectric slab is Ad. The slab possesses total dipole moment = qi d. therefore, by definition, the polarization density is written as


Dielectrics-12-Dielectric Strength
Consider a dielectric slab is inserted between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor. As the potential difference across the plates of the capacitor is increased, the strength of applied electric field increases. The molecules of the dielectric undergo more and more stretching. If potential difference is increased gradually, a stage will reach when the electrons break up from the molecules of the dielectric. As a result, the electric break down in the dielectric slab takes place and so the dielectric loses its identity and becomes conducting. It gives the concept of Dielectric strength under the topicDielectrics-12, thus,
The dielectric strength of a dielectric medium is defined as the maximum value of electric field or potential gradient that can be applied to the dielectric medium without its electric breakdown.
Dielectrics-12-SI unit of dielectric strength
The SI unit dielectric strength is same as that of electric field, thus, Vm-1 (volt per meter) or kVm-1
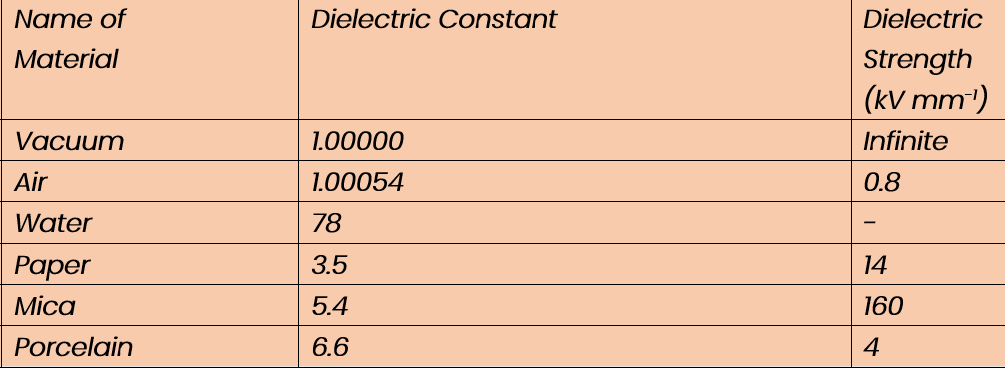
Dielectrics-12-table of dielectric constants and Dielectric strength of different materials
Dielectrics-12-Summary
- Polar atoms- The center of gravities of Negative charge distribution (extranuclear electrons) and positive charge distribution (Protons within the nucleus) do not coincide and so behave like an electric dipole. Such atoms possess asymmetric distribution of charges about their centers.
- Non-Polar atoms- The center of gravities of Negative charge distribution (extra nuclear electrons) and positive charge distribution (Protons within the nucleus) coincide and so do not behave like an electric dipole. Such atoms possess spherical symmetric distribution of charges about their centers.
- Polarization- The stretching of the atoms of the dielectrics resulting in to the displacement of C. Gs. of positive and negative charge distribution under the effect of an external applied electric field.
- Polarization density- The dipole moment induced in a dielectric medium per unit its volume under the effect of an electric field is called polarization density.
- Dielectric Constant- It is the Ratio of the strength of the applied electric field to the strength of reduced value of electric field on inserting the dielectric slab between the plates of a capacitor.
- Dielectric Strength- It is the maximum value of the electric field or the electric potential gradient that can be applied to the dielectric medium without its electric breakdown.
- Unit of dielectric strength is V m-1
- The dielectric medium when inserted between the plates of a capacitor its capacity by K times where K is the dielectric constant of the dielectric medium.
Dielectrics-12-Frequently asked questions and their answers
- Ques: Distinguish between polar and non- polar dielectrics. Ans: The dielectrics whose molecules possess some permanent electric dipole moment, even when electric field is not applied, is called polar dielectric. On the other hand, the dielectric whose molecule do not possess permanent dipole moment is called non polar
- Ques: How will you define polarization? Ans: The stretching of the atoms of the dielectrics resulting in to the displacement of C. Gs. of positive and negative charge distribution under the effect of an externally applied electric field.
- Ques: What is a dielectric? Ans: Dielectrics-12 is an insulator that does not conduct electricity, but on applying electric field, induced charges are produced on its faces.
- Ques: Why does the electric field inside a dielectric decrease when it is placed in an external electric field? Ans: When a dielectric is placed in an external electric field, then it undergoes polarization and the electric field so produced due to polarization of the dielectric is opposite to the external electric field. Hence, the electric field inside the dielectric gets reduced.
- Ques: The dielectric constant of a conductor is taken to be infinitely large. Explain why.? Ans: When a conductor is placed inside an electric field, the field inside the conductor becomes zero due to conduction and the reduced field is zero. As the dielectric constant of the dielectric is the ratio of the strength of applied electric field to the reduced value of electric field, so it will be infinite for the conductor.
- Ques: Write down the relation between dielectric constant and electric susceptibility. Ans: The susceptibility and the dielectric constant of a dielectric medium are related to each other by the relation. K = 1 + X (Ki)
- Ques: Define dielectric strength of the medium .Ans: The dielectric strength is the maximum value of the electric field that a dielectric medium can withstand without its breakdown