Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE-magnetic field of earth.
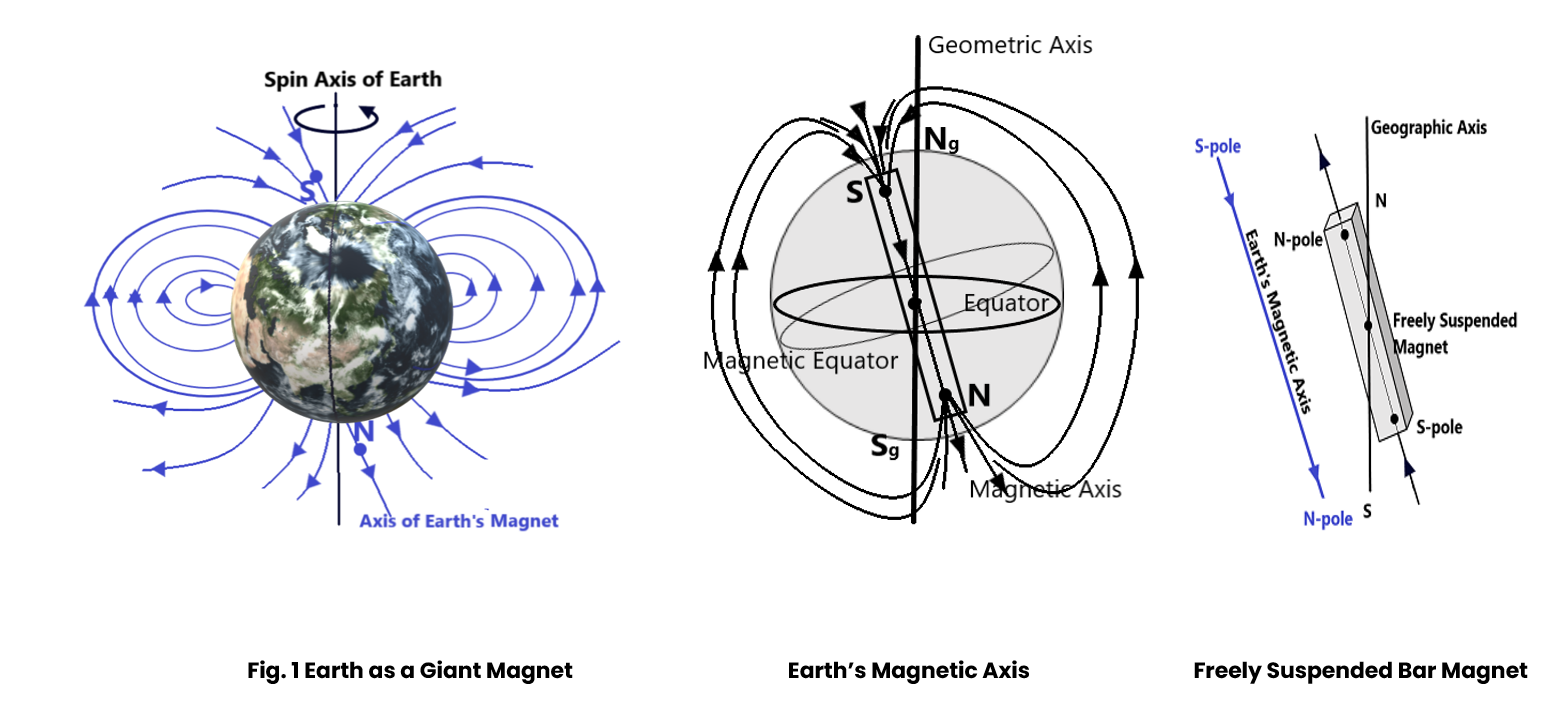
It was invented by William Gilbert, in his paper “De Magnete” published in 1600, suggested the earth behave like a giant magnet. His theory regarding the earth being a huge magnet was supported by the result of the experiments, he did at that time. When a bar magnet is freely suspended through a torsion less unspun thread, it rests itself in the direction parallel to the magnetic field of earth such that its N- pole points towards the geographical north While the S-pole points towards the geographical south.
The magnetic field of earth resembles with that of the bar magnet in all respect such that its magnetic axis (N-S line) makes an angle of about 20 degrees with the geometric axis/ spin axis of earth.
Some Important Terms-Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE
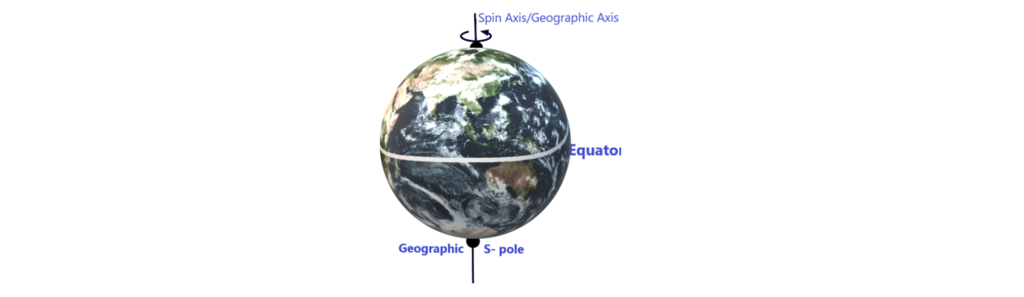
- Geographic Axis: This is also called the spin axis of the earth and it is defined as an axis about which our earth spins or rotates as shown above in the figures and the points on the surface of the earth where it passes through are called as geographic poles.
- Equator: The circle, of maximum radius, on the surface of the earth and perpendicular to this is called as equator.
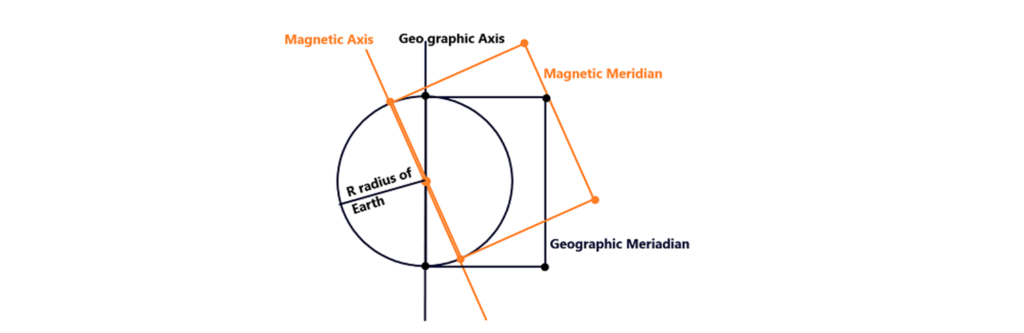
3. Geographic and Magnetic Meridian: Geographic meridian is defined as the vertical plain passing through the geographic axis / spin axis of earth as shown in the figure below highlighted in black colour. While, the magnetic meridian is defined as the vertical plain passing through the magnetic axis of earth as shown in the figure below highlighted in yellow colour.
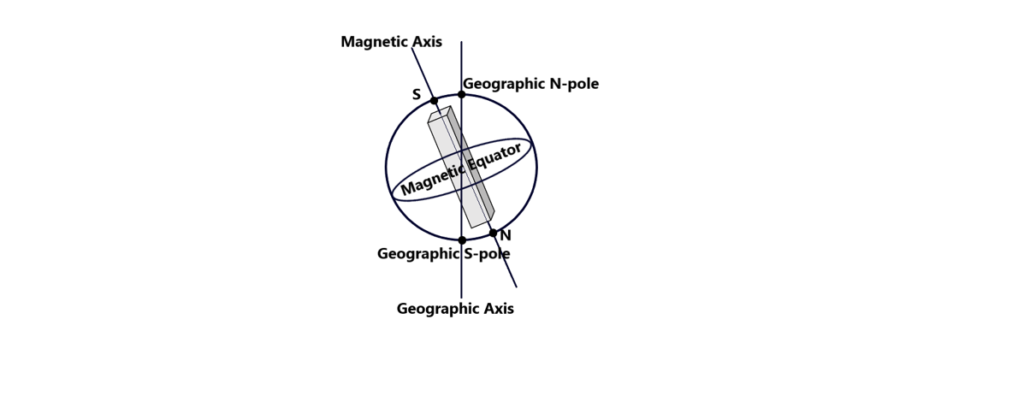
4. Magnetic Axis and Magnetic poles:
Magnetic Axis and Magnetic poles: Earth is assumed to have a giant bar magnet placed inside it which accounts for the existence of its magnetic field and its other magnetic activities. The axis of this giant magnet in side the earth is called magnetic axis and the points on the surface of earth where the magnetic axis cuts, are called magnetic poles. The largest circle on the surface of earth perpendicular to the magnetic axis is called magnetic equator.
Global Position of Earth’s Magnet-Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE
On the basis of numerous experiments conducted by various scholars and the observations available so far, it has been established that the earth exhibits magnetic behavior and looks as if huge magnet is placed inside it. This is called as earth’s magnet.
The axis of the magnet of earth (magnetic axis) does not coincide the geographic axis but is tilted through an angle of about 20-21 degrees from geographic axis as shown in the fig. below
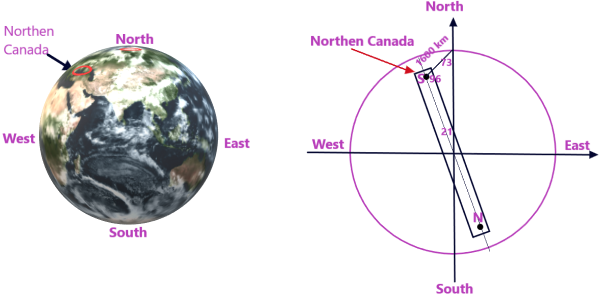
The Magnetic N-pole and S-pole are widely separated from the geographical poles of the earth. The magnetic south pole (S-pole) in presently located in Northern Canada. And this magnetic S-pole is at about 1600 km form the geographical north at 74 degree north latitude and about 96 degree west longitude. N-pole of earth’s magnet is located diametrically opposite to the S-pole at 75degree south latitude and 84 degree east longitude.
Origin of Earth’s Magnetism-Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE
There are various theories suggested by scholars and pioneers in the field of electricity and magnetism that give explanations in regard to the origin of earth’s magnetism. Some of these are discussed here.
- A pioneer scholar Professor Blackett, upon the basis of his intensive studies and experiments, suggested a theory of the origin of the magnetic field of the earth. This theory said that the earth’s magnetism is due to the molten charged metallic fluid in the core of the earth within the radius of about 3500 km. These charged particles behave like the current loops as the earth rotates about its own axis. Because the magnetic fields surround electric currents. So we conclude that circulating electric currents in the Earth’s molten metallic core are the origin of the magnetic field. The magnitude of the earth’s magnetic field at the surface of the earth is measured to be about 0.5 Gauss.
- The cosmic rays, the phenomenon of radioactivity, and the high energy radiations coming from the sun ionize the gases present in the atmosphere of the earth. As the earth continuously rotates about its axis, strong electric currents are set up due to the ionized charged particle in the earth’s atmosphere, causing the earth to be magnetized.
- The third view regarding the origin of earth’s magnetism is the dynamo effect. The core of the earth consists of metals like iron and nickel in molten state. As the earth rotates continuously, the relative motion sets up with the fluid of iron and nickel. Thus, due to the rotation of the earth, it acts as the dynamo and so becomes magnetized.
Magnetic Elements in earth’s magnetism-Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE
Magnetic elements in the topic- Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE-are the physical quantities which evaluate the intensity of earth’s magnetic field completely in magnitude as well as in direction. There are mainly three types of magnetic elements.
- Magnetic Declination:
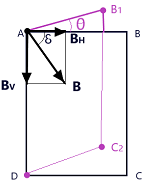
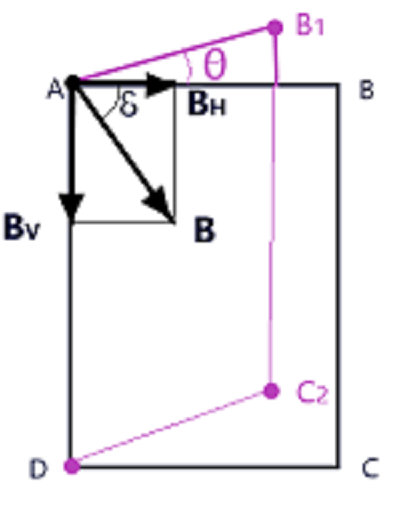
Magnetic declination at a place is defined as the angle that the geometric meridian makes with the magnetic meridian and is denoted by theta.
As in figure given here, ABCD and A B1 C2 D are representing the magnetic meridian and geographic meridian respectively, then as per the definition of the magnetic declination, it will be represented by the angle BA B1
2. Magnetic Inclination:
Magnetic inclination at a place is defined as the angle that the direction of earth’s total magnetic field B makes with the direction of horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field and is denoted by delta. Thus, as per the fig. given here
3. Horizontal Component of earth’s magnetic field:
This is defined as component of earth’s magnetic field along the horizontal direction and is denoted by BH.

NEUTRAL POINTS AND TO FIND MAGNETIC MOMENT OF A BAR MAGNET-Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE
A bar magnet is associated with its own magnetic field as shown in the fig. given below. When the magnetic field due to a bar magnet is plotted on a paper, we use a magnetic needle that shows the direction of the field at each point. As this experiment is done on the earth, therefore, the magnetic needle will act under the combined effect of the magnetic field due to the bar magnet and the field due to earth. In the electric field so plotted consists of two points where the two fields, due to bar magnet and due to earth nullify each other. These points are called Neutral Points
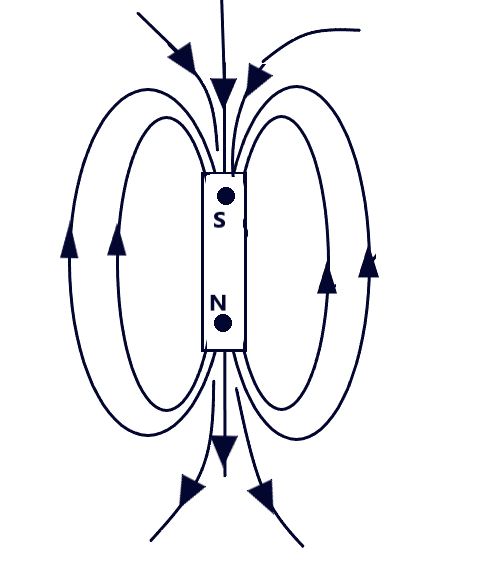
Thus, a neutral point in the magnetic field of a bar magnet is that point where the field due to the bar magnet is completely neutralized by the horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field.
Therefore, at a neutral point the magnetic field due to a bar magnet is equal to the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field in magnitude and opposite in direction.
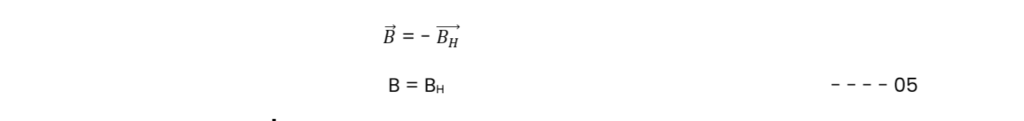
Application of Neutral Points-Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE
The magnetic moment of a bar magnet(in the topic Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE) is experimentally determined by plotting its magnetic field and noting the positions of the neutral points. Then we use the eqn. 05, to determine analytically the magnetic moment of the bar magnet in two cases
Case 1. When the bar magnet is placed with its N-pole pointing geographical north or S-pole of earth’s magnet
When the bar magnet is placed with its N-pole pointing geographical north or S-pole of earth’s magnet and draw its magnetic field that is the field modified with earth’s field, we get the two neutral points N1 and N2 on the equatorial line at distance l from the bar magnet on its both sides as shown in fig. below.
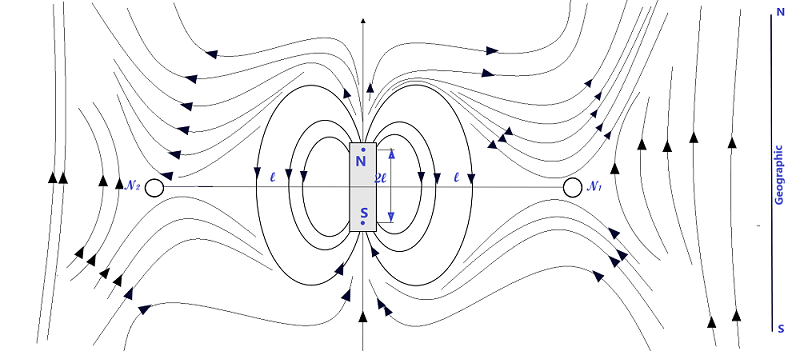
The magnetic field due to the bar magnet at the point on the equatorial line distant l from the bar magnet is

Case 2: When the magnet is placed with its S-pole towards the north of the earth.
When the bar magnet is placed with its S-pole pointing geographical north or S-pole of earth’s magnet and draw its magnetic field that is the field modified with earth’s field, we get the two neutral points N1 and N2 on the axial line of the bar magnet at distance l from the bar magnet on its both sides as shown in fig. below.
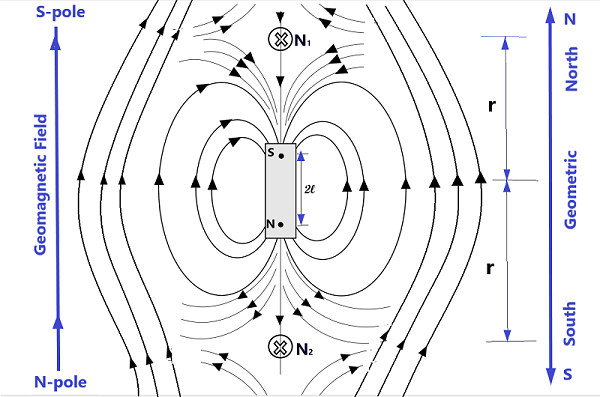
The magnetic field due to the bar magnet(in the topic Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE) at the point on the axial line distant l from the bar magnet is

From comparing these two cases we note that the neutral points in case 1 were found at the points on the equatorial line. When the magnet is rotated through an angle of 180 degree, and the neutral points are rotated through 90 degree and appear on the axial line. Thus we conclude that when the magnet is rotated through 180 degree, the neutral points turn through 90 degree.
Frequently asked questions and their answers Section -1-Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE
- Ques: The Earth’s core is known to contain iron, but geologists do not regard this as a source of a magnetic field. why?
- Ans: The temperature inside the earth is so high that. Impossible for the iron core. To remain as a magnet and act. And act as the source of a magnetic field. The magnetic field due to the Earth is considered to be due to the circulating electric currents induced in the iron in its molten state and other conducting materials inside the Earth
- Ques: Why does a bar magnet always stand in NS- direction, when suspended freely? Ans: It is assumed that a huge magnet is lying deep inside the Earth with its S- pole towards the geographical north and N- Pole towards the geographical south as in topic Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE
- Ques: What is a geographic meridian? Ans: A vertical plane passing through the geographical NS- line is called the geographical meridian.
- Ques: What is a magnetic meridian? and what is geomagnetic equator? Ans: A vertical plane passing through the magnetic axis of the earth is called the magnetic meridian. The great circle on the earth’s surface whose plane is perpendicular to the magnetic axis is called the magnetic equator.
- Ques: Name the parameters needed to completely specify the earth’s magnetic field at a point. Ans: At a point on the earth’s surface. The parameters needed to completely specify the Earth’s magnetic field are. Right nation dip. And the original component of Earth’s magnetic fields.
- Ques: Define the angle of magnetic declination at a place. Ans: Declination at a place is the angle between the geographic and magnetic meridian.
- Ques: At a certain location in Africa, a compass needle points, 15 degrees west of the geographic north. What is the angle of declination at that point? Ans: Theta equal to 15 degrees. west of the geographic north (Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE)
- Ques: How does the knowledge of declination in the topic Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE at a place help in navigation Ans: Declination at a place is the angle between the geographic and magnetic meridians. By knowing the declination, the ship can be steered in the required direction, so as to reach the destination.
- Ques: A small magnet is pivoted to move freely in the magnetic meridian. At what place on the Earth’s surface will the magnet be vertical? Ans: At the magnetic poles of the Earth as in topic Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE
- Ques: What would be the direction of a compass needle when placed exactly at the geometric north pole. Ans: It will stand vertical with the north pole downwards and the South Pole upwards.(Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE)
Frequently asked questions and their answers Section –2-Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE
- Ques: Which direction would a compass point to? If located right on the geomagnetic north or South Pole. Ans: The magnetic compass needle can point in any direction on the geomagnetic north or south pole. It is because the horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field is zero at these points.(Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE)
- Ques: Define the angle of the dip at a given place under the topic Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE Ans: Dip at a place is defined as an angle made by the direction of the earth’s total magnetic field with the horizontal direction.(Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE)
- Ques: What is the value of the angle of dip at any place situated on the magnetic equator of the earth? Ans: It is zero degrees. (Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE)
- Ques: The angle of dip at a location in southern India is about 18 degrees. What do you expect, a greater or lesser dip angle in Britain? Ans: Britain is close to the magnetic north pole. Therefore, the angle of dip is greater in Britain than in India. It is about 70 degrees.(Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE)
- Ques: What is the expected value of dip at the magnetic poles of the earth? Ans: It is 90 degrees. The magnet becomes vertical at both the magnetic north and south pole.
- Ques: What do you mean by a neutral point in a magnetic field? Ans: A neutral point in the magnetic field due to a bar magnet is defined as that point where the magnetic field due to the magnet is completely neutralized by the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field
- Ques: It is found that the neutral points lie along the axis of the magnet placed on a table. What is the orientation of the magnet with respect to the earth’s magnetic field? Ans: The neutral points lie along the axis of the magnet when the magnet is placed along the magnetic NS-line with its north pole towards the south of the Earth.(Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE )
- Ques: A magnet is placed with its north pole, towards the north of the Earth. Predict the position of the neutral points. Ans: on the equatorial line of the magnet.
- Ques: A magnet is placed with. Pull towards the south of the Earth Position of the neutral points. Ans: On the axial line of the magnet (Earth’s Magnetism-12 CBSE)




One Comment