Problem: 16
The variation of the momentum of a particle and the de-Broglie wavelength associated with it is represented by which of the following figures?
M.C.Qs. wave nature of matter
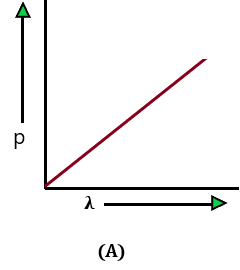

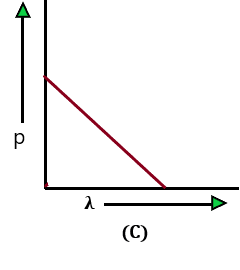
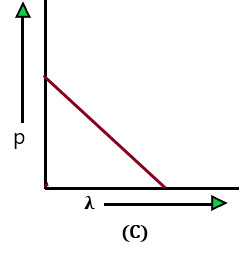
Problem: 17
What should be the accelerating voltage required for electrons to produce the hard X-rays of minimum wavelength of 10-11 m to study the fractures of bones?
M.C.Qs. wave nature of matter
(A) > 124.2 k V
(B) < 124.2 kV
(C) =120 kV
(D) Between 60 kV and 80 kV
Problem: 18
The energy of a photon is equal to the kinetic energy of a proton. The. energy of the photon is E. The ratio of the wavelengths of the photon and the proton will be
M.C.Qs. wave nature of matter
(A) E1/2
(B) E0
(C) E-2
(D) E-1
Problem: 19
A particle of mass M and at rest decays into two particles of masses, m1 and m2 having non- zero velocities. The ratio of the de-Broglie wavelengths of the particles is
M.C.Qs. wave nature of matter
(A) m2/m1
(B) m1/m2
(C) 1
(D) ( m2/m1)1/2
Problem: 20
The momentum of photon of frequency v and velocity c will be
M.C.Qs. wave nature of matter
(A) hv/c
(B) hv/c2
(C) v/c
(D) hv c2
Problem: 21
An electron and a photon have same de-Broglie wavelengths, then the velocity of the photon is
(A) greater than that of electron
(B) less than that of electron
(C) equal to that of electron
(D) None of the above
Problem: 22
An electron is accelerated through a potential difference of 150 V. The de-Broglie wavelength of the electron waves will be
M.C.Qs. wave nature of matter
(A) 4.8 A0
(B) 108 A0
(C) 1 A0
(D) 10 A0
Problem: 23
The de-Broglie wavelength 𝛌 of a particle is related to its kinetic energy E as
M.C.Qs. wave nature of matter
(A) 𝛌 ∝ E
(B) 𝛌 ∝ (E)1/2
(C) 𝛌 ∝ 1/(E)1/2
(D) 𝛌 ∝ 1/E
Problem: 24
The crystal structure can be studied by electron diffraction, by neutron diffraction both. In order to have the same de-Broglie wavelength 𝛌, for the electron of mass me and neutron of mass mn , their velocities should be in the ratio (electron velocity / neutron velocity) as.
M.C.Qs. wave nature of matter
(A) mn/me
(B) me/mn
(C) mn me
(D) 1
Problem: 25
An electron microscope gives higher magnification than an optical microscope, because of the reason that
(A) the velocity of the electrons is smoother than that of the light.
(B) the electron have smaller wavelength than that of the light wave.
(C) more powerful lenses are used in the electron microscope.
(D) the electron have more energy than the light particle.
Problem: 26
An electron microscope has a higher magnification is of the order of
M.C.Qs. wave nature of matter
(A) 102
(B) 104
(C) 105
(D) 107
Problem: 27
A photoelectric surface is illuminated successively by monochromatic light of wavelength 𝛌 and 𝛌/2. If the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons in the second case is 3 times that in the first case, the work function of the surface of the material is——. (plank’s constant = h and velocity of light = c)
(A) hc/2𝛌
(B) hc/𝛌
(C) hc/3𝛌
(D) 2hc/𝛌
Problem: 28
An electron is accelerated from the rest through a potential difference of V volt. If the de-Broglie wavelength is 1.227 x 10-2 nm. The potential difference V is
M.C.Qs. wave nature of matter
(A) 104 V
(B) 105 V
(C) 103 V
(D) 10 V [NEET- 2020]
Problem: 29
Light of frequency 1.5 times the threshold frequency is incident on a photo sensitive material. What will be photo- electric current if the frequency is halved and the intensity is doubled?
(A) Four times
(B) Doubled
(C) Halved
(D) Zero [NEET- 2020]
Problem: 30
The work function of a photo sensitive material is 4.0 eV. The longest wavelength of light that can cause photoemission is approximately
(A) 3100 nm
(B) 31 nm
(C) 3.3 nm
(D) 310 nm [NEET- 2019]
